What is intelligent automation (IA), and how does it differ from robotic process automation (RPA)? While IA and RPA are sometimes used interchangeably, these are two distinct practice areas.
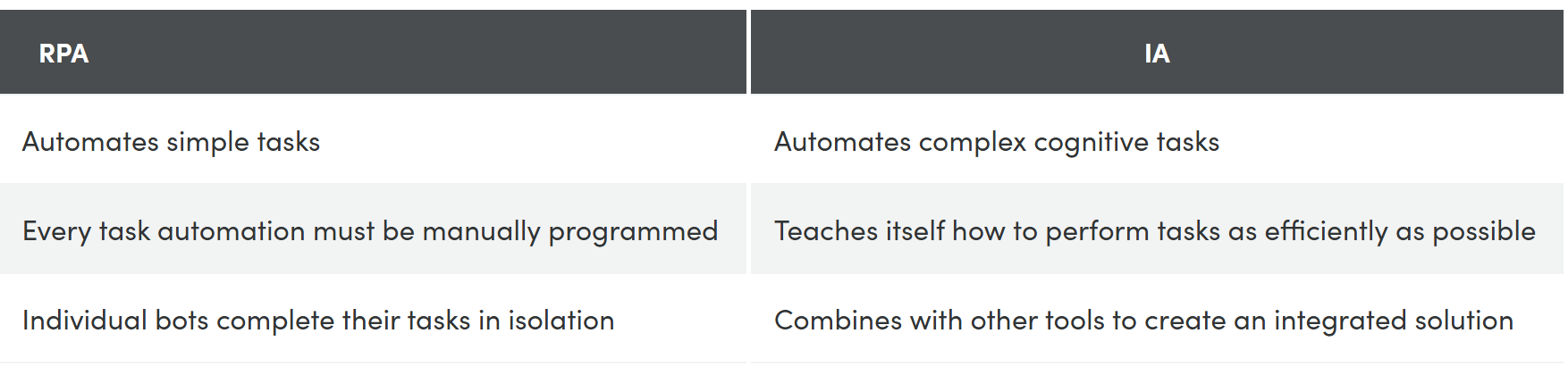
RPA is a technology that automates simple, digital tasks like completing forms, organizing documents, or performing simple searches and queries.
Intelligent automation is the process of integrating AI with systems in order to automate more complex tasks, generate insights, and learn from experience.
This creates some fundamental differences between IA and RPA and what they can do.
Simple vs complex
RPA can only complete simple tasks, like organizing, moving, and storing data or files. Most of these tasks are manual, time-consuming, and highly repetitive—and worth automating—but do not require cognition, interpretation, or analysis of content.
IA can complete complex work that requires higher-order thinking. For example, it can “read” the text within a file and categorize it based on intent, or analyze website usage data to find patterns and suggest improvements that would increase conversion rates.
Programmed vs self-learning
RPA can only work within a set of rules. Either an RPA system is programmed to complete a few specific steps, or a user records a task and the RPA solution copies their behavior. Either way, RPA can only repeat what it’s told or shown to do.
IA can teach itself how to complete tasks, and can improve its performance the more it repeats a task. While RPA will always repeat a task the same way every time, IA can identify more efficient steps to reach the same outcome at higher accuracy rates.
Siloed vs integrated
RPA technology largely works in isolation. An RPA system is typically self-contained and has everything it needs to complete its tasks. Each bot is programmed to complete one simple task that does not connect directly with anything other bots are doing.
IA is an integrated solution. Different elements of the solution can learn from each other, and the solution can combine a wide range of cognitive capabilities like computer vision, business process management, and character recognition from external tools.
In sum: Intelligent automation (IA) vs. robotic process automation (RPA) is a false debate. Intelligent automation is a modern process that layers over robotic process automation and lets you automate more complex workflows, and robotic process automation is a component of intelligent automation. Overall, intelligent automation and robotic process automation are two components of a single system for automating modern, complex, digital workflows.
Intelligent automation upgrades robotic process automation–giving you even greater speed, cost savings, and performance boosts across more processes.